Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects up to 1 in 10 women worldwide.
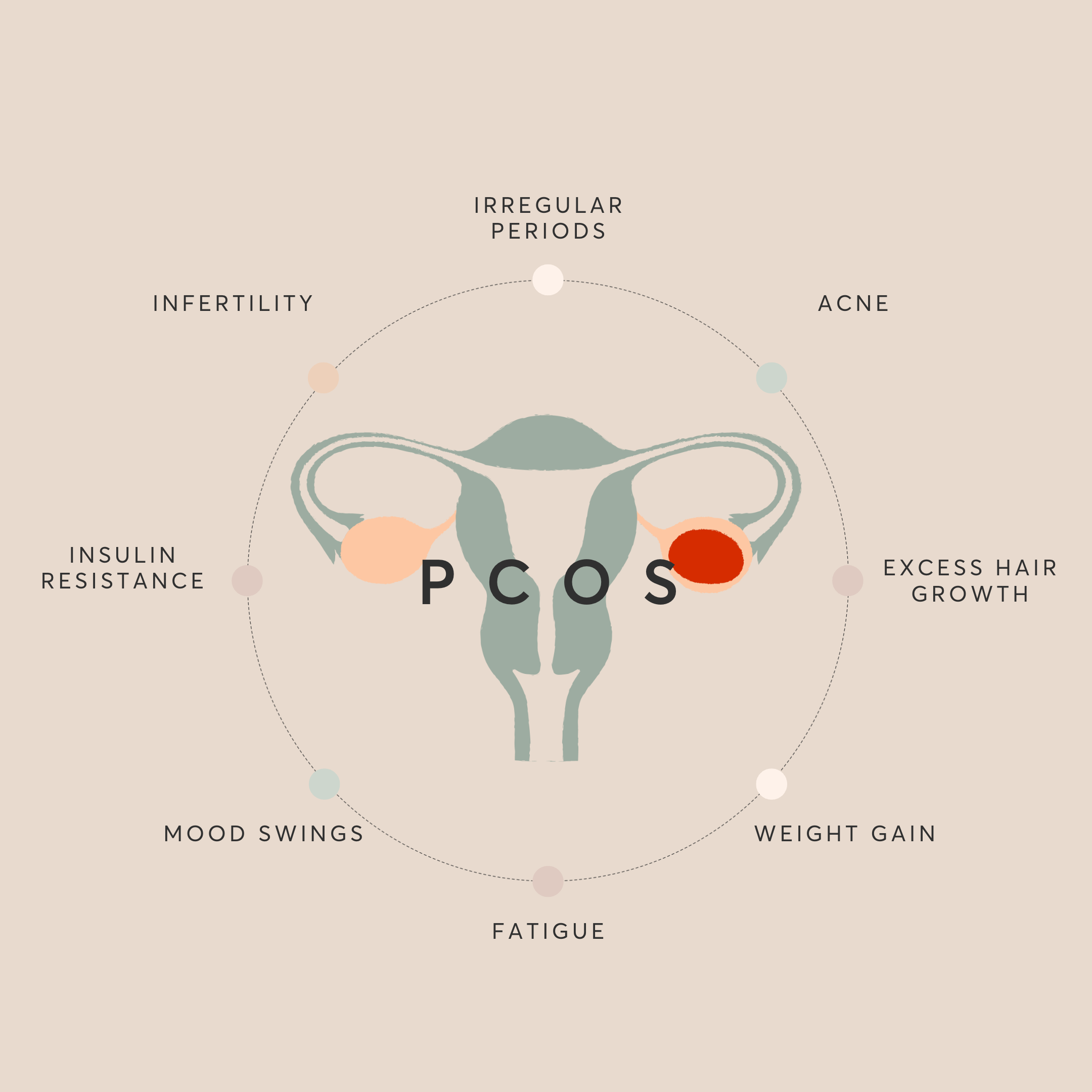
PCOS is often characterised by the presence of small cysts, or fluid-filled sacs, on the ovaries, which can lead to a range of symptoms, including irregular periods, infertility, acne, excess hair growth, and weight gain. However, it is important to note that not all women with PCOS have cysts on their ovaries, and the symptoms can vary from person to person.
There are several different types of PCOS, each with its own unique set of symptoms and underlying causes. Insulin-resistant PCOS is the most common type, and is associated with high levels of insulin in the blood, which can cause weight gain, metabolic problems, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Post-pill PCOS is a type of PCOS that can develop after discontinuing hormonal contraceptives, and is often characterised by irregular periods and hormonal imbalances. Inflammatory PCOS is a type of PCOS that is associated with chronic inflammation in the body, which can lead to a range of symptoms, including acne, weight gain, and insulin resistance. Adrenal PCOS is a type of PCOS that is associated with high levels of androgens, or male hormones, in the blood, which can cause acne, excess hair growth, and irregular periods.
Despite its many different forms, PCOS can be effectively managed with a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and supplements. In particular, a healthy diet and regular exercise are important for managing PCOS symptoms and improving overall health. This means eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, and avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats. It is also important to stay hydrated and limit alcohol and caffeine intake.
Despite these challenges, there are several steps that women with PCOS can take to increase their chances of conceiving. One option is to work with a fertility specialist who can help identify the best course of treatment, such as fertility medications or assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilisation (IVF). Another option is to use ovulation prediction kits or track basal body temperature to help identify the most fertile days of the menstrual cycle. Maintaining a healthy weight and managing insulin resistance can also improve fertility and increase the likelihood of successful conception.
While trying to conceive with PCOS can be a challenging journey, there are many success stories to inspire hope. Take for example, Rachel, who had struggled with infertility for years before being diagnosed with PCOS. She began working with a fertility specialist who prescribed a combination of medication and dietary changes. With perseverance and dedication, Rachel was able to conceive naturally and gave birth to a healthy baby boy.
Another example is Sarah, who had been diagnosed with PCOS and was advised to undergo IVF. While the process was difficult, Sarah and her partner were able to conceive and give birth to twins. Despite the challenges that come with trying to conceive with PCOS, stories like these remind us that it is possible to overcome and achieve the dream of starting a family.
Trying to conceive with PCOS can be a complex and challenging journey. However, with proper management and support, women with PCOS can increase their chances of conceiving and starting a family. Whether through lifestyle changes, medication, or assisted reproductive technologies, there are many paths to success. So don't lose hope, and remember that you are not alone in this journey.
Here’s a few lifestyle changes you can make to improve your chances of conceiving and reducing the symptoms:
Follow a healthy diet:
A healthy and balanced diet is key to managing PCOS symptoms and improving fertility. A diet rich in whole foods, including plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, lean protein sources, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates, can help regulate insulin levels, reduce inflammation, and support healthy hormone production. Consider working with a registered dietitian to create a personalised eating plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
Incorporate regular exercise:
Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, promote weight loss, and reduce stress levels - all of which can help improve PCOS symptoms and boost fertility. Aim to incorporate both aerobic and strength-training exercises into your routine, with a goal of at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week.
Manage stress levels:
High levels of stress can negatively impact hormone balance and interfere with ovulation, making it more difficult to conceive. Consider incorporating stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Limit processed and sugary foods:
Consider supplementation:
Certain nutrients and supplements may be beneficial for women with PCOS who are trying to conceive. For example, inositols, a type of carbohydrate, may help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate hormone production. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseed, may also help reduce inflammation and improve fertility. Speak with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine if supplementation may be right for you.
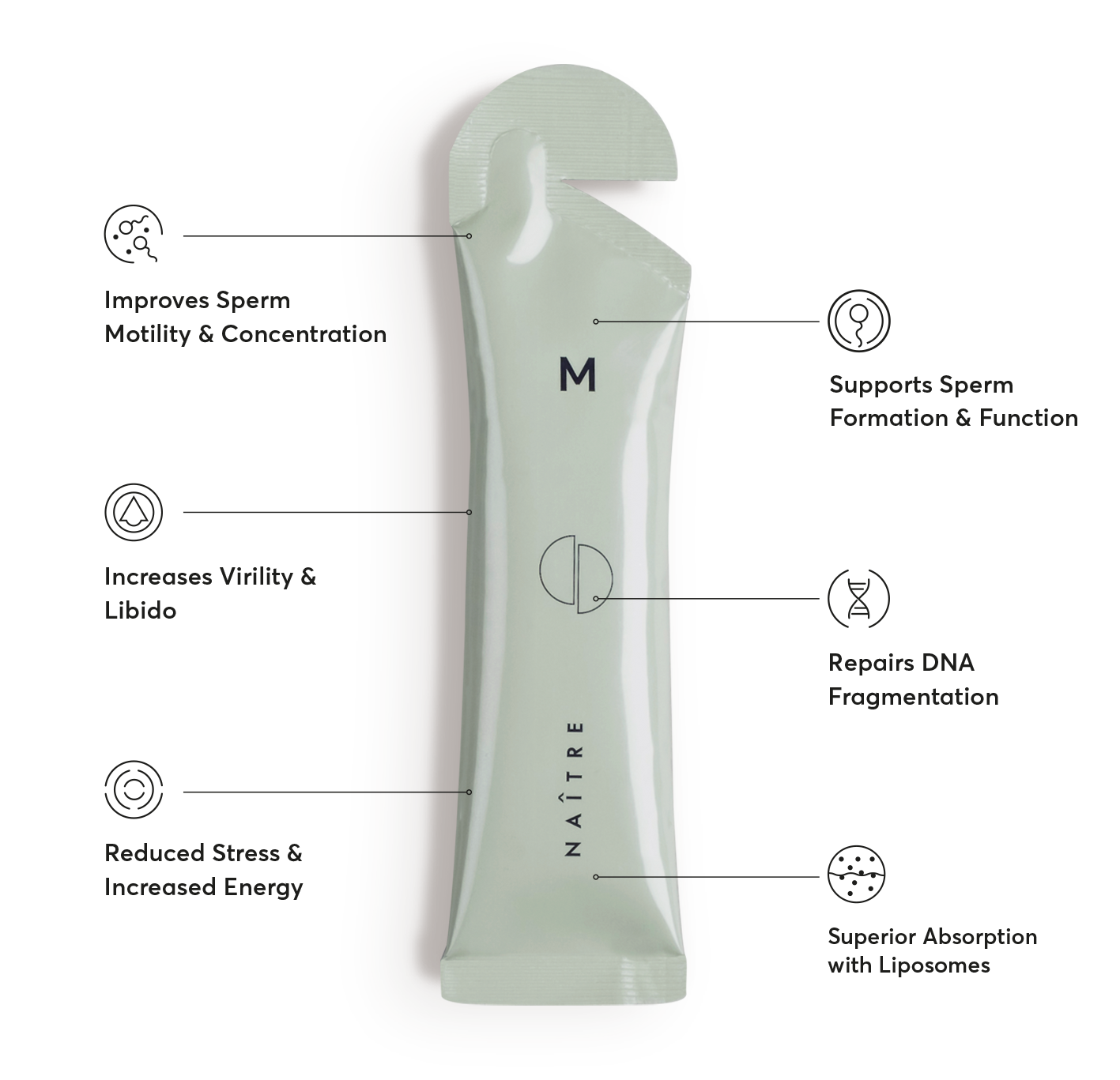
Several of the ingredients in Naître's liposome-based formulas can potentially help alleviate PCOS symptoms. Here are a few examples:
Chromium:
Chromium is a mineral that has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which can be beneficial for women with PCOS. Insulin resistance is a common symptom of PCOS and can contribute to weight gain and difficulty conceiving.
Magnesium:
Magnesium is an important mineral that plays a role in regulating insulin levels and improving glucose metabolism. Studies have shown that women with PCOS tend to have lower magnesium levels than women without PCOS, so supplementing with magnesium may be helpful.
Zinc:
Zinc is a mineral that is involved in many metabolic processes in the body, including hormone production and immune function. Zinc deficiency has been linked to insulin resistance and higher androgen levels, both of which are common in women with PCOS.
N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC):
NAC is an amino acid that has been shown to improve insulin resistance, reduce inflammation, and regulate menstrual cycles in women with PCOS. It may also improve egg quality and increase the chances of ovulation.
Vitamin D:
Vitamin D deficiency is common in women with PCOS and has been linked to insulin resistance, inflammation, and reduced fertility. Supplementing with vitamin D may help improve these symptoms.
Maca Extract:
Maca is a root vegetable that has been used traditionally for its medicinal properties. It may help improve menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve fertility in women with PCOS.
It is worth noting that while these ingredients have shown promise in improving PCOS symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle.
Conclusion:
While PCOS can be a challenging condition to manage, it is important to remember that there are many effective strategies that can help alleviate its symptoms and increase the chances of conceiving. By following a healthy diet, incorporating regular exercise, managing stress levels, and considering targeted supplementation, women with PCOS can take an active role in their health and fertility. With the right support and resources, it is possible to overcome the obstacles presented by PCOS and achieve a successful pregnancy.